What is Blood Sugar: Will Be No More Now 24
What is Blood sugar?
What is Blood sugar? The simplest answer to this is “The amount of glucose that is present in the bloodstream is referred to as blood sugar, or blood glucose.“. The body’s cells use glucose, a simple sugar, as their main energy source. It comes from the food we eat, especially the carbs that our bodies break down into glucose as they digest.
After entering the bloodstream, the pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which helps carry glucose to all of the body’s cells.
Blood sugar regulation is essential for general health. When fasting, normal blood sugar levels normally fall between 70 and 99 mg/dL, and two hours after eating, they should be less than 140 mg/dL.
Disorders including hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can result from improper regulation of these levels.
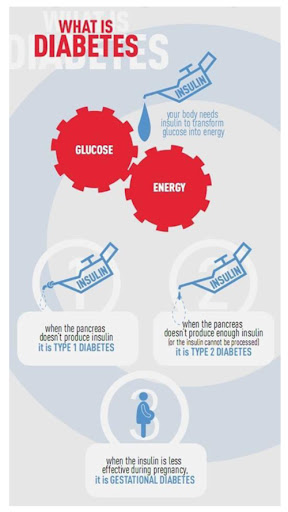
Diabetes mellitus, a collection of metabolic illnesses defined by either inadequate insulin production (Type 1 diabetes) or inefficient insulin utilization by the body (Type 2 diabetes), is typified by persistently elevated blood sugar levels.
A combination of dietary changes, exercise, and occasionally medication is used to control blood sugar.
For those with diabetes, routine blood glucose monitoring is crucial to preventing consequences including renal failure, nerve damage, and cardiovascular disease. An essential aspect of metabolic health and general wellbeing is knowing and sustaining appropriate blood sugar levels.
Why is blood sugar important?
Since blood sugar gives the body’s cells energy, it is essential. Cells cannot operate correctly in the absence of sufficient glucose. Blood sugar regulation is necessary for good health and the smooth operation of many body systems.
What causes blood sugar levels to fluctuate?
- Blood sugar levels can vary due to a number of reasons, such as:
- Nutrition: Consuming foods high in carbs causes blood sugar levels to rise.
- Exercise: By utilizing glucose as fuel, exercise helps lower blood sugar levels.
- Hormones: The main hormones that control blood sugar levels are glucagon and insulin.
- Stress and illness: These can raise blood sugar levels because they trigger the release of hormones associated with stress.
- Drugs: A number of drugs have the potential to alter blood sugar levels.
Follow our Digiknowledge.co.in page for the latest updates about technology, bikes, cars, sports, lifestyle, and many more.
What are the types of blood sugar disorders?
Hyperglycemia: Elevated blood sugar levels, frequently linked to diabetes.
Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar, which can happen to diabetics because of too much insulin or other things.
What is high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)?
An excessively high blood sugar level is known as hyperglycemia. Blood sugar is commonly described as being higher than 180 mg/dL two hours post-meal or higher than 130 mg/dL during a fast. Diabetes, certain drugs, and diseases are common reasons.
What is low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)?
When blood sugar falls too low—typically below 70 mg/dL—hypoglycemia results. Hormonal deficits, prolonged fasting, heavy alcohol intake, high insulin, and some drugs are among the causes.
How can we control blood sugar levels?
Controlling blood sugar levels can be achieved by:
- Diet: Consuming meals that are well-balanced and contain the right amounts of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Exercise: Getting regular exercise aids in blood sugar regulation.
- Medication: Blood sugar levels can be managed with the use of insulin and other diabetes drugs.
- Monitoring: Testing blood sugar levels on a regular basis to monitor levels.
- Stress management: Blood sugar control can be achieved through stress management techniques like yoga and meditation.
What are the complications of uncontrolled blood sugar?
Severe consequences can result from uncontrolled blood sugar, including:
Cardiovascular disease: Higher risk of strokes and heart attacks.
Damage to the nerves: May cause tingling, discomfort, and loss of feeling.
Damage to the kidneys: Causing chronic renal disease or failure.
Damage to the eyes: Raising the risk of diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts.
Foot issues: Severe infections and amputations can result from poor circulation and nerve damage.
How do different types of diabetes affect blood sugar?
Type 1 Diabetes: High blood sugar levels are caused by the body’s immune system attacking the pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Patients need to be on insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: Excessive blood sugar is caused by the body’s lack of insulin or its resistance to it. Changes in lifestyle, oral medicines, and occasionally insulin are used to manage it.
Pregnancy-related gestational diabetes raises the chance of later acquiring Type 2 diabetes but typically goes away after delivery.
What role does insulin play in blood sugar regulation?
The hormone insulin, which the pancreas produces, aids in the body’s cells’ absorption of blood glucose. Insufficient insulin causes glucose to stay in the bloodstream, which raises blood sugar levels. For the treatment of diabetes, especially Type 1, insulin therapy is essential.
What research is ongoing regarding blood sugar management?
Current investigations consist of:
Building closed-loop insulin delivery systems with automated insulin level adjustments would create an artificial pancreas.
New drugs: developing pharmaceuticals with reduced adverse effects and increased effectiveness.
Genetic studies: Comprehending the hereditary components of diabetes and blood sugar control.
Researching how different diets affect blood sugar levels is known as nutrition research.
Innovations in technology: Increasing the precision and usability of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices.
Groundbreaking achievement in diabetes treatment announced by researchers in China
China has declared that cell treatment has produced the first-ever documented cure for diabetes. The patient, who is 59 years old, underwent a novel cell transplant in 2021 and has not needed medication since 2022. This is a ground-breaking accomplishment.
Although the synopsis does not specify the precise form of diabetes treated, these novel cell therapies are frequently directed towards Type 1 diabetes, in which the pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin are attacked by the body’s immune system. Nevertheless, based on the methodology employed, it might also apply to Type 2 diabetes.
The management of diabetes may be completely changed if cell therapy is effectively scaled up and repeated. It provides millions of people with diabetes with hope for a long-term cure, thereby increasing their quality of life and maybe lowering the long-term health consequences linked to the condition.
This news could have a significant impact on the diabetes community worldwide because it presents a fresh and promising approach to the disease’s cure.
It highlights the significance of ongoing research and innovation in the management of diabetes and may encourage additional funding and cooperation in the area.
Can lifestyle changes prevent blood sugar problems?
Yes, making lifestyle changes including eating well, exercising frequently, staying at a healthy weight, and giving up tobacco use can greatly lower the risk of developing blood sugar issues and enhance the treatment of pre-existing diseases.
What is cell therapy for diabetes?
Transplanting beta cells that produce insulin into a patient is the standard approach to cell therapy for diabetes. These cells can be produced by sophisticated biotechnological techniques, stem cell derivation, or donor genesis. The intention is to help the body once again manufacture and use insulin as a hormone.
What is a normal blood sugar level?
A person without diabetes will have a glucose tolerance test of 140 mg/dl or less, an A1C test of less than 5.7%, and a fasting blood glucose test of less than 100 mg/dl.




