Public Health: Link between Stress and Heart Disease 24
Public Health
Comprehensive attention is necessary due to the enormous public health risk that the complex link between stress and heart health poses. Stress is a commonplace aspect of contemporary life and can cause a range of physical and psychological reactions that have a significant negative influence on cardiovascular health.
Prolonged stress sets off a series of physiological reactions that include a raised heart rate, blood pressure, and the release of stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
While these reactions are useful in emergency situations, they can be harmful if they persist over time, which can lead to the onset and worsening of cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
High levels of stress are correlated with a higher risk of cardiac problems like hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke, according to epidemiological studies that have repeatedly demonstrated this connection. Furthermore, stress can aggravate heart health by encouraging bad habits like smoking, eating poorly, and not exercising.
By supporting healthy lifestyle choices, stress management techniques, and supportive surroundings, public health efforts seek to reduce these risks. In order to create interventions and policies that effectively lower the burden of cardiovascular illnesses and eventually improve population health outcomes, it is imperative that one has a thorough understanding of the intricate relationship between stress and heart health.
Improving and protecting population health through environmental manipulation and control is the goal of public health, a multidisciplinary field with roots in medical science and philosophy. Using coordinated efforts and well-informed decisions, this discipline seeks to prevent illness, extend life, and promote health in communities, businesses, the public and private sectors, and individuals.
How can we improve public health?
- The enhancement of living conditions is essential to public health. A few examples of how housing affects health outcomes are respiratory ailments, lead poisoning, and mental health disorders. These are only a few of the conditions that can arise from substandard housing. So, a top concern for public health is making sure that housing is both safe and sufficient.
- Another pillar is water supply management. For the purpose of preventing waterborne illnesses and enhancing general health, access to clean, safe drinking water is crucial. The main goals of public health initiatives are to ensure appropriate water treatment and distribution, safeguard water sources from contamination, and encourage sanitary habits.
- Nutrition is just as important as food safety. Public health programs work to guarantee that food sources are wholesome, contaminant-free, and available to all facets of society. This includes handling concerns related to food security, educating the public about good eating practices, and regulating the procedures involved in the production and distribution of food.
- Public health professionals seek to improve people’s lives by tackling these environmental factors, which will lower the prevalence of disease and raise people’s standards of living in their communities.
Follow our Digiknowledge.co.in page for the latest updates about technology, bikes, cars, sports, lifestyle, and many more.
Link between Stress and Heart Disease
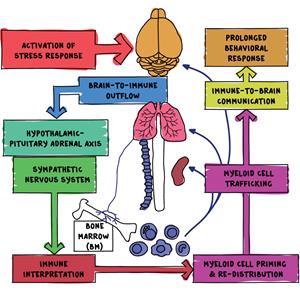
New findings clarify the severe effects of heart failure on the body and provide insight into an intriguing phenomenon known as “stress memory.” According to this new theory, those who suffer from heart failure may be more susceptible to future heart failure and other related health problems because of the long-lasting effects of the physiological stress the illness causes on the body.
Hematopoietic stem cells—which produce blood and immune cells like macrophages that are essential for heart health—are at the forefront of this finding. After cardiac failure, researchers have found changes in these stem cells’ DNA modification, which suggests a long-lasting stress-induced effect.
The fundamental aspect of this method is the inhibition of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), a crucial signaling pathway, in hematopoietic stem cells when heart failure occurs. One important regulator of cellular activities, such as macrophage formation and function, is TGF-β. Its inhibition interferes with macrophages’ ability to differentiate and operate normally, which reduces their capacity to defend cardiac tissue.
This dysregulated immune response can have effects on general health in addition to the heart. In the body’s fight against infections, the reduction of inflammation, and tissue healing, macrophages have a variety of functions. Their decreased function as a result of stress memory brought on by heart failure may therefore make them more vulnerable to infections, inflammation-related illnesses, and poor wound healing.
Targeted treatment strategies are made possible by an understanding of the molecular mechanisms driving stress memory in heart failure.
Researchers hope to create novel approaches to lessen the long-term effects of heart failure and enhance patient outcomes by clarifying the complex interactions among stress, immunological dysregulation, and heart health.
The study’s findings ultimately highlight the significance of holistic methods in the management of cardiovascular illnesses, incorporating psychological and physiological factors to improve patient care and quality of life.
How do we improve public health and well-being?
- Public health is being advanced globally, as evidenced by the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations, which place a high priority on improving everyone’s health and well-being. Positively, new studies show that life expectancy is increasing and that by 2050, it will rise by about 4.5 years globally.
- Together, public health initiatives have reduced mortality rates and prevented sickness, especially in the case of cardiovascular problems, which is largely responsible for this encouraging trend.
- Heart disease continues to be the leading cause of mortality globally in spite of these developments, making it a persistent global health concern. Heart failure affects alarmingly many people—an estimated 26 million people—which emphasizes the critical need for ongoing study and treatment.
- The tendency for heart failure to reoccur frequently, with complications including renal and muscle issues, is very concerning. Recognizing the complex nature of this problem, Japanese researchers have set out to identify the fundamental processes causing organ degradation and illness recurrence.
- Their investigation aims to clarify the complex relationship between systemic organ function and cardiovascular health in order to pinpoint preventative measures that can break the cycle of recurrence and lessen related health risks.
- This study has the potential to guide focused interventions that not only improve outcomes for heart failure patients but also improve general health and well-being by exploring the underlying reasons for disease recurrence and organ dysfunction.
- Researchers, healthcare professionals, politicians, and communities can work together to convert scientific findings into effective treatments that will move us closer to the SDGs’ goal of a society where everyone is healthier and more equitable.
What is the relationship between health and well-being?
Health is influenced by both wellbeing and wellbeing itself. Many physical health outcomes, including better immune system response, greater pain tolerance, longer lifespans, cardiovascular health, slower disease progression, and reproductive health, are correlated with wellbeing.
What is the link between stress and heart disease?
Heart disease can be caused by stress in a number of different ways. “Prolonged or ongoing stress can raise the body’s inflammatory response, which in turn can lead to an increase in plaque accumulation in the arteries and other issues like coronary artery disease,” explains Dr. Lampert.
What are the diseases caused by stress?
There is a connection between different psychological and physical disorders and chronic stress. Conditions including high blood pressure, heart disease, obesity and metabolic syndrome, Type II diabetes, and arthritis are a few examples of these.
What is the most harmful stress?
Chronic stress—which arises from encountering stressors on a regular basis—can be extremely harmful to your health. Prolonged stress can lead to headaches, sleeplessness, anxiety, weight gain, soreness, and elevated blood pressure. Relationships are a common source of long-term stress.





Pingback: Energy Drinks-Heart Attack Risk: Any Connection? 24 - Digiknowledge
I’m glad to hear that you find the content helpful and enjoyable! If you have any specific topics you’re interested in or questions you’d like to explore further, feel free to ask