Hydrogen Engine: The Next-Generation Fuel 24
The hydrogen engine
The hydrogen engine is a game-changer for automotive technology, paving the way for powerful and ecologically sustainable cars of the future. Hydrogen engines employ hydrogen gas as a clean, sustainable fuel source as opposed to traditional internal combustion engines, which run on fossil fuels. With just water vapor produced as a byproduct, this cutting-edge technology generates power by burning hydrogen or using hydrogen fuel cells.
As a result, hydrogen engines are an emission-free option that helps meet the urgent need to cut greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change.
When compared to electric vehicles, hydrogen engines have a number of appealing benefits, such as great efficiency, quick refueling periods, and the possibility for long driving ranges. Furthermore, hydrogen is the most prevalent element in the cosmos, providing an almost infinite.
Due to their remarkable power and accuracy, hydraulic engines are essential to both automobiles and industry. They improve the efficiency and safety of cars‘ braking, steering, and lifting systems.
Because they offer great torque and fine control for lifting, pressing, and moving big loads, hydraulic engines are useful in the heavy machinery, construction, and manufacturing industries.
They increase production by lowering maintenance costs and downtime due to their durability and efficiency. Hydraulic engines continue to be crucial for advancing industrial and automotive applications as the need for dependable, high-performance systems increases.
Hydrogen technology is particularly noteworthy since it can be easily incorporated into the current infrastructure and has a far smaller carbon footprint than other options as the automobile industry moves toward more environmentally friendly alternatives.
A bright future is indicated by continuous developments and growing investment in hydrogen infrastructure, even in the face of obstacles like the dearth of widely distributed refueling stations and the high cost of manufacture. Using hydrogen engines could revolutionize the transportation sector and move society toward a more sustainable and clean environment.
In this article, we are going to focus on some of the most important points, such as
Benefits of hydrogen fuel engines, Hydrogen fuel cell vs hydrogen combustion engine, Hydrogen engine conversion kits, challenges of hydrogen engine technology and the future of hydrogen-powered vehicles Hydrogen engine vs electric engine , Hydrogen fuel stations availability, etc.
How does a hydrogen engine work?
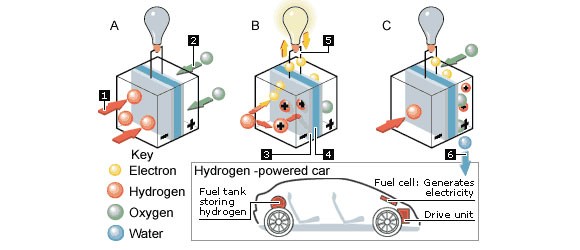
Hydrogen gas is the fuel used in hydrogen engines. Hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen combustion engines are the two primary kinds. Similar to gasoline in conventional engines, hydrogen burns in hydrogen combustion engines to produce power and water vapor as byproducts. Hydrogen combines with oxygen in hydrogen fuel cells to create energy, which drives an electric motor.
Benefits of Hydrogen-Fuel Engines
- Only water vapor is released by motors running on hydrogen fuel. They have the potential for longer driving ranges and faster refueling periods than electric vehicles. Produced from a variety of sources, including renewable energy, hydrogen is abundant.
- A hydrogen engine is a modified internal combustion engine that works on hydrogen fuel instead of conventional gasoline. It is often referred to as a hydrogen internal combustion engine (HICEV). When comparing hydrogen engines to conventional engines, it is possible to cut CO2 emissions from the exhaust by almost 99%.
- Neither carbon monoxide nor volatile organic compounds nor particulate particles are released by them.
- Hydrogen has special combustion properties that allow it to burn cleanly and effectively in engines. Because of its fast flame speed and broad range of flammability (between 4 and 75% of hydrogen by volume in air), hydrogen can burn at up to five air-fuel ratios for extremely lean combustion. These same traits, however, can also result in technical issues at high engine loads, such as a greater propensity to pre-ignite the hydrogen-air mixture and a rise in NOx output.
- To assist the automotive and transportation industries in addressing these issues, the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) established the Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (H2-ICE) Consortium.
- The Hyundai Nexo and the Toyota Mirai were the two hydrogen-powered vehicles that were readily accessible in certain areas as of 2021.
But some nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are produced by hydrogen engines, can cause haze in cities during the summer.
You can find detailed information about Toyota Innova Hycross here. Please click.
A brief comparison between a fuel hydrogen cell and a hydrogen engine.
Electric motors are powered by hydrogen fuel cells, which produce electricity by reacting hydrogen with oxygen. It’s clean and really effective. Just as conventional gasoline engines, hydrogen combustion engines provide mechanical power by burning hydrogen, but they only release water vapor into the atmosphere.
A brief comparison between a hydrogen engine and an electric engine.
Electric engines depend on power stored in batteries, whereas hydrogen engines (fuel cells) generate electricity while operating on hydrogen. Longer range and faster refueling times are advantages of hydrogen vehicles, but electric vehicles now have a more developed infrastructure and cost-effective operation.
What are hydrogen engine conversion kits?
The ability to run conventional gasoline or diesel engines on hydrogen is provided by hydrogen engine conversion kits. In order to handle the hydrogen fuel, these kits usually comprise storage tanks, control systems, and hydrogen injectors. Switching to hydrogen can help cut down on pollution and reliance on fossil fuels.
Challenges and Future of Hydrogen Engine Technology.
The development and storage of hydrogen are expensive, there is a lack of infrastructure for refueling, and strong safety precautions are required because hydrogen is flammable. Further, one of the biggest challenges is still creating effective ways to produce hydrogen.
As technology develops and costs come down, the future of hydrogen-powered automobiles is bright. Rising investments in renewable energy and hydrogen infrastructure could lead to a rise in the use of hydrogen vehicles, which would help cut down on fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
There are currently very few hydrogen fueling stations, mostly located in certain areas, such as California, as well as some sections of Europe and Japan. For hydrogen vehicles to be widely used, this infrastructure must be expanded, which will take careful planning and substantial financial resources.
Why don’t we use hydrogen engines?
Because of the high expense of manufacture and storage, hydrogen-fueled automobiles are not widely used. The process of electrolysis, which needs a lot of energy, is the main way to produce hydrogen gas. Since fossil fuels are still used to manufacture the majority of hydrogen, cutting carbon emissions is counterproductive.
Why is hydrogen fuel unsafe?
Because hydrogen is a very combustible gas and can explode or cause fires if not handled carefully, it is employed in fuel cells. The gas hydrogen has no taste, smell, or color. While propane and natural gas are odorless as well, a sulfur-containing odorant called Mercaptan is added to both gases to enable leak detection.
What are the three disadvantages of hydrogen fuel?
Hydrogen is an extremely combustible and explosive material that is difficult to move around. Although hydrogen may be produced by hydrolyzing water, the process is exceedingly costly.
Are hydrogen cars available in India?
The Indian auto industry does not now provide any hydrogen-powered vehicles for purchase. The intention of a number of automakers to introduce these cars to the Indian market has been stated.
How long will a hydrogen engine last?
All essential fuel cell parts, such as the fuel cell stack, compressor, hydrogen Page 16 tanks, battery packs, and fueling control units, are likewise covered by warranties from the automakers. The fuel cell stacks are intended to last the vehicle’s lifetime, or between 150,000 and 200,000 miles.
Can a normal engine run on hydrogen?
Sure. Diesel and hydrogen internal combustion engines (ICE) function similarly. The same method by which gasoline or diesel are burned in a conventional internal combustion engine is also used to burn hydrogen. Hydrogen engines produce almost no pollutants at all, including no soot or volatile organic compounds.
Do hydrogen engines need oxygen?
Electricity for a motor is produced by hydrogen fuel cells using hydrogen and oxygen. In order to avoid the detrimental effects of gas or electric vehicles, companies like Toyota are investing in this fuel of the future. It is believed that 11,000 hydrogen-powered vehicles are currently in use.




