Green Mediterranean Diet-24
Green Mediterranean Diet
The Green Mediterranean Diet is a way of eating that incorporates the fundamentals of the conventional Mediterranean diet with a focus on plant-based diets, sustainability, and environmental awareness. This creative version tackles the ecological effects of dietary choices while also promoting health and well-being.
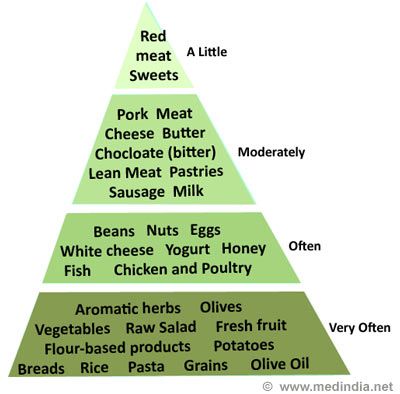
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and olive oil, and low in processed foods and red meat, is the classic Mediterranean diet, which is well-known for its heart-healthy properties.

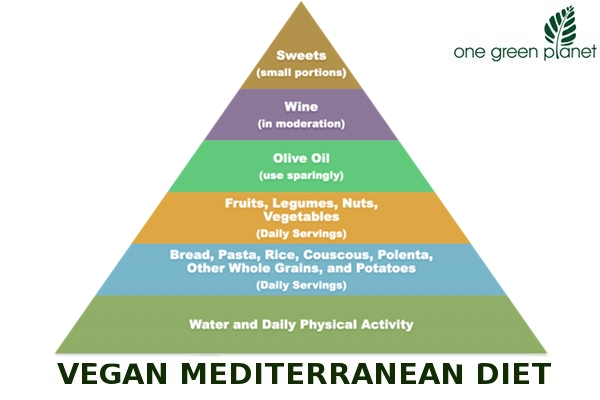
Building upon these principles, the Green Mediterranean Diet reduces carbon emissions even further by emphasizing plant-centric diet and making thoughtful food choices.
What are the Base of the Green Mediterranean Diet?
Plant-based foods
Plant-based foods are the foundation of the Green Mediterranean Diet. The main players in terms of important nutrients, fibre, and antioxidants include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes. These plant-based diets improve general health and are linked to a decreased risk of long-term illnesses.
As with the traditional Mediterranean diet, olive oil is still an essential component. It has a lot of monounsaturated fats, which are good for the heart. Choosing extra virgin olive oil increases its potential health advantages in addition to adding flavor to meals.
Consumption of seafood
The Green Mediterranean Diet emphasizes the consumption of seafood in a sustainable manner. Omega-3 fatty acids strengthen cardiovascular health, and fish and seafood are great sources of them. Ethically sourced seafood guarantees long-term seafood availability while also contributing to the preservation of marine ecosystems.
Minimized Red Meat Intake:
The Green Mediterranean Diet goes one step further by promoting a reduction in the intake of red and processed meats, even though the conventional Mediterranean diet already supports a limited consumption of red meat. Legumes and tofu, which are plant-based sources of protein, can make great substitutes.
Healthy Eating Selections:
Being mindful goes beyond the plate. The Green Mediterranean Diet urges individuals to be aware of the environmental impact of their food choices. The guiding principles of the diet are supported by choosing seasonal produce that is purchased locally and by endorsing environmentally responsible farming methods.
Follow Our Digiknowledge.co.in Page for Latest update about Bikes, Cars, Sports, , Life style and many more.
What are the Health Benefits of the Green Mediterranean Diet?
Heart health
Heart health is benefited by the Green Mediterranean Diet’s concentration on plant-based foods and heart-healthy fats, especially those found in fish and olive oil. This food pattern has been repeatedly demonstrated to lower the risk of heart disease in studies.
Weight management
Eating a diet high in fiber-rich foods encourages satiety, which aids in maintaining a healthy weight. Additionally, emphasising nutrient-dense, whole diets promotes general wellbeing.
Decreased Inflammation:
Chronic inflammation, which is linked to a number of illnesses, can be lessened by the anti-inflammatory qualities of plant-based diets and the omega-3 fatty acids found in seafood.
Better Blood Sugar Regulation:
One benefit of the Green Mediterranean Diet is that it supports complex carbohydrates, which are present in whole grains and legumes and help regulate blood sugar levels. For people who are managing or at risk of diabetes, this is very helpful.
Cancer Prevention:
A decreased risk of specific types of cancer may be attributed to the rich supply of antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables as well as the possible preventive effects of certain plant chemicals.
What are the Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Green Mediterranean Diet?
Decreased Carbon Footprint:
The Green Mediterranean Diet naturally lowers the carbon footprint connected with food production by emphasising plant-based foods and sustainable seafood options. Diets heavy in plant-based foods often have less of an impact on the environment than diets high in animal products.
Encouragement of Local Agriculture:
Choosing seasonal and locally grown produce helps local farmers by lowering transportation-related emissions. This is consistent with the diet’s emphasis on sustainability and mindfulness.
Preservation of Marine habitats:
Selecting seafood that comes from sustainable sources guarantees that people are helping to preserve marine habitats. When customers make educated decisions, overfishing and damaging fishing methods are lessened.
Decreased Demand on Land Resources:
If more people consume a plant-based diet, the demand for land resources will decline because plant agriculture often uses less space than animal agriculture. This contributes to addressing issues with habitat loss and deforestation.
What are the Tips for Adopting the Green Mediterranean Diet?
Fill Your Plate with Colour:
Try to include a variety of vibrant fruits and vegetables. These give a spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Select Whole Grains:
Refined grains are not as healthy as whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat. These offer additional fibre and minerals.
Add Plant Proteins:
Don’t forget to include plant-based protein sources in your diet, such as tofu, beans, lentils, and chickpeas.
Make Sustainable Seafood Your Top Priority:
When including seafood, go for selections that are sourced sustainably. See recommendations from resources such as the Seafood Watch guide from the Monterey Bay Aquarium.
Mindful Portioning:
Even when consuming healthful foods, exercise caution when determining portion amounts. By doing so, you can avoid overindulging and manage your weight.
Test-Out Plant-Based Cooking:
To make the switch to a more plant-centric diet appealing, try out plant-based recipes and cooking methods.
Buy seasonal and locally sourced produce whenever you can to support local farmers. By doing this, the environmental impact of food transportation is lessened while simultaneously promoting local agriculture.
Keep Yourself Hydrated:
According to the Green Mediterranean Diet, water is still the preferred beverage. In addition to avoiding the needless environmental impact of alternative beverage options, it is vital for general health.
In conclusion, the Green Mediterranean Diet combines the tried-and-true guidelines of the conventional Mediterranean diet with an emphasis on plant-based eating and environmental awareness to provide a comprehensive approach to health and sustainability.
Following this food pattern can help people maintain the health of the world in addition to improving their own wellbeing.
The Green Mediterranean Diet serves as an effective reminder that the foods we eat have a significant impact on both our own health and the health of the planet we live on.
Can you drink green tea on Mediterranean diet?
Three to four cups of green tea each day and a dish of walnuts every day are two more pillars of the diet. Of course, the standard components of a Mediterranean diet—whole grains, fresh veggies, and olive oil—should also be included.
What’s the difference between the Mediterranean diet and the Green Mediterranean diet?
One of the main distinctions between the classic and green Mediterranean diets is that the former allows red and processed meats on occasion, while the latter removes them entirely.
What food is not allowed on the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet forbids the intake of processed foods, refined sugars, refined carbohydrates, and trans fats. The diet also restricts the consumption of red meat and high-fat dairy items.




